Fire bricks are very common in the manufacturing units. They are often referred to as refractory bricks in the manufacturing processes. You can say that they are specialized products formulated to bear high temperatures and tough conditions. A wide range of industrial uses requires these products, especially in environments with high temperatures.
This blog post discusses what fire brick is made out of and discuss its composition and uses in various industries.
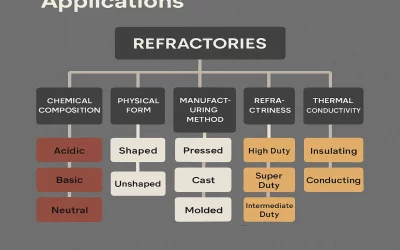
What are Fire Bricks?
Fire bricks are designed to withstand the high temperatures that would normally weaken ordinary masonry materials. Such bricks play a crucial role in use such as in furnaces, kilns, fireplaces, and incinerators. Fire bricks primarily serve the purpose of insulation and safeguarding structural integrity under heat.
The importance of fire bricks goes beyond temperature resistance alone; they also help in energy efficiency by reducing heat loss. Knowing the materials that make up fire bricks is crucial for industries that depend on such products for operational efficiency and safety.
Composition of Fire Bricks
Exactly what is a fire brick made out of? Fire bricks consist of the following components.
Silica
This is the primary ingredient in fire bricks, comprising 60-96% of the material. Silica has a high melting point and that is around 3200°F. Quality like this provides structural stability under extreme heat.
Alumina
Typically making up 2-36% of the composition, alumina enhances the heat resistance of fire bricks. It melts at approximately 3800°F. Very high alumina components are crucial for applications requiring sustained high temperatures.
Fluxing Agents
These include lime, magnesia, iron oxide, and alkalis. Although present in smaller quantities like 2 to 5 percent. Components help lower the melting point of silica and alumina, facilitating the manufacturing process.
- The production of fire bricks is a careful and systematic process, which makes the end product resistant to harsh conditions.
- It starts with the digging up of raw materials from the ground, which are usually fire clay, silica, and alumina.
- These are then allowed to weather naturally, a process that improves their quality by breaking down impurities and allowing moisture to seep in.
- After being adequately weathered, the materials are combined with water to form workable consistency for preparation for moulding.
- This heat-treated mix is then molded carefully into forms of bricks while ensuring uniformity and accuracy.
- Lastly, the moulded bricks are kiln-dried under regulated temperatures in order to produce vitrification—a process which cements the bricks and bestows upon them their incredible resistance to heat.
Types of Fire Bricks
Fire bricks can be classified into several categories based on their composition and intended use.
Normal Fire Bricks: These are produced from natural fire clay blended with crushed clay and sand. They have 50-75% silica and 20-40% alumina. They are used for general purposes and can withstand temperatures of 1600°C.
Silica Bricks
These contain approximately 95% silica. They are best used for acid lining furnaces for glass manufacturing and metalworking because they can withstand temperatures of 2000°C.
High Alumina Bricks
These contain a higher percentage of alumina (30-50%) and are designed for extreme conditions found in industrial applications like steelmaking furnaces. They can stand temperatures up to 1800°C.
Acid Resistant Bricks
Specifically formulated to resist acidic environments, these bricks are vital in industries where chemical exposure is a concern.
Applications of Fire Bricks
Fire bricks find extensive use across various industries due to their unique properties:
Industrial Furnaces: Fire bricks line the interiors of furnaces used in metal processing and glass manufacturing, providing thermal insulation while protecting structural integrity.
Kilns: In pottery and ceramics industries, fire bricks help maintain high temperatures necessary for firing clay products without damaging kiln walls.
Chimneys and Fireplaces: Fire bricks are used in residential settings to construct fireplaces that can withstand high heat while preventing heat loss.
Pizza Ovens and Wood Stoves: Their ability to retain heat makes them ideal for cooking appliances that require consistent high temperatures.
The Importance of Refractory Bricks
Refractory bricks are essential for any application involving high-temperature processes. Their ability to withstand thermal shock and rapid changes in temperature ensures longevity and reliability in demanding environments.
Low Thermal Conductivity: This property helps retain heat within furnaces or kilns while keeping external surfaces cooler, enhancing energy efficiency.
Durability Against Chemical Erosion: Many refractory bricks are designed to resist chemical attack from acids or other corrosive substances encountered in industrial processes.
Ganeshas Refractory Solutions
When it comes to sourcing premium fire bricks, Ganeshas stands out as a reputable manufacturer committed to producing durable refractory materials tailored for various applications.
You can choose from ordinary fire bricks, high alumina options, and acid-resistant bricks tailored to specific industry requirements. Ganeshas ensures that all products undergo rigorous quality control processes to guarantee performance under extreme conditions.
To Sum Up
Knowing what fire brick is composed of is crucial for industries dependent on these resources for operation. From their composition—mainly silica and alumina—to their varied uses across industries such as metalworking, building, and ceramics, fire bricks are instrumental in maintaining safety and efficiency in high-temperature settings.
By investing in good refractory materials like those provided by Ganeshas, companies can improve their working capabilities while protecting their infrastructure from the hardships brought about by intense heat.